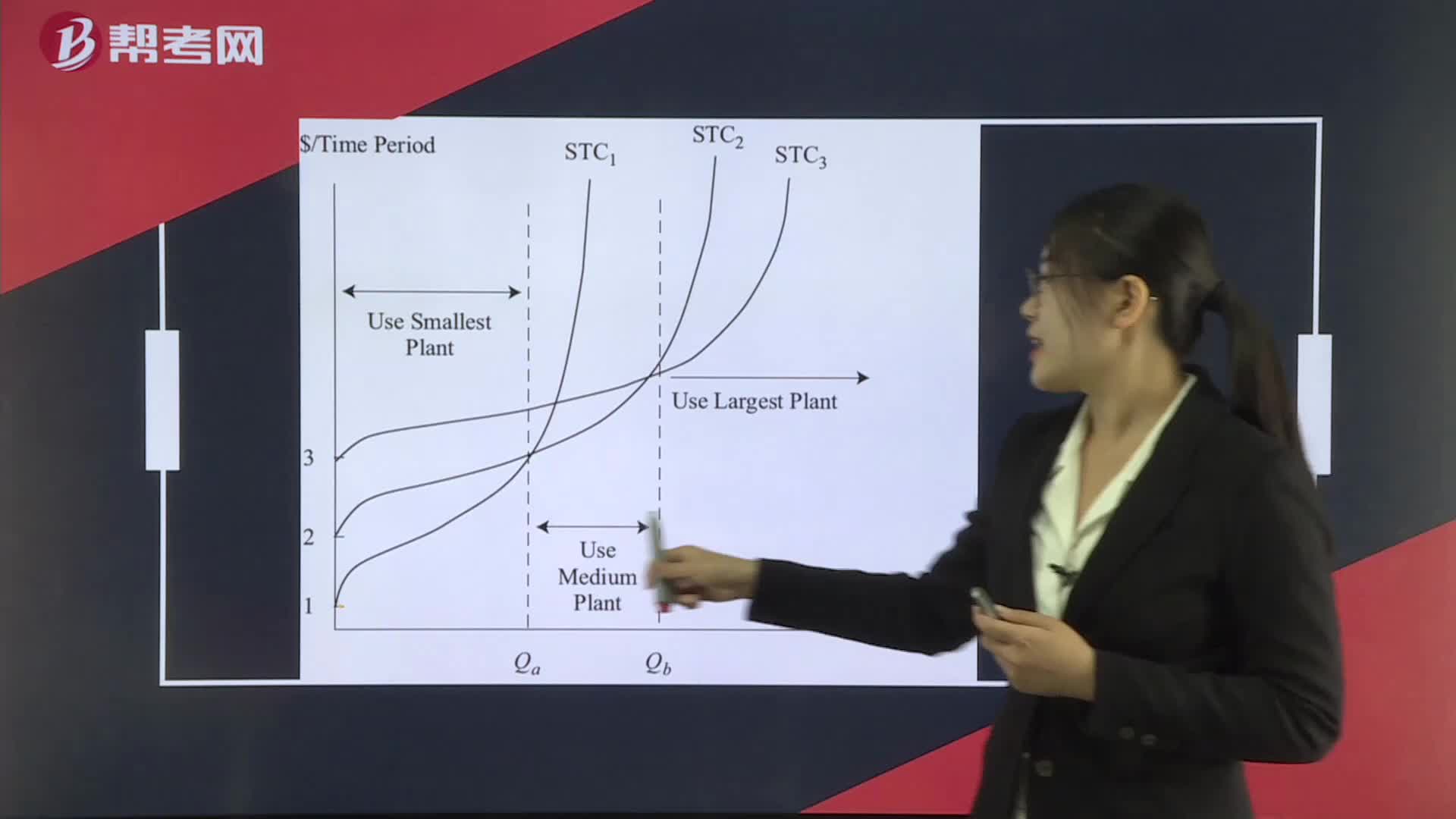
Short- and Long-Run Cost Curves
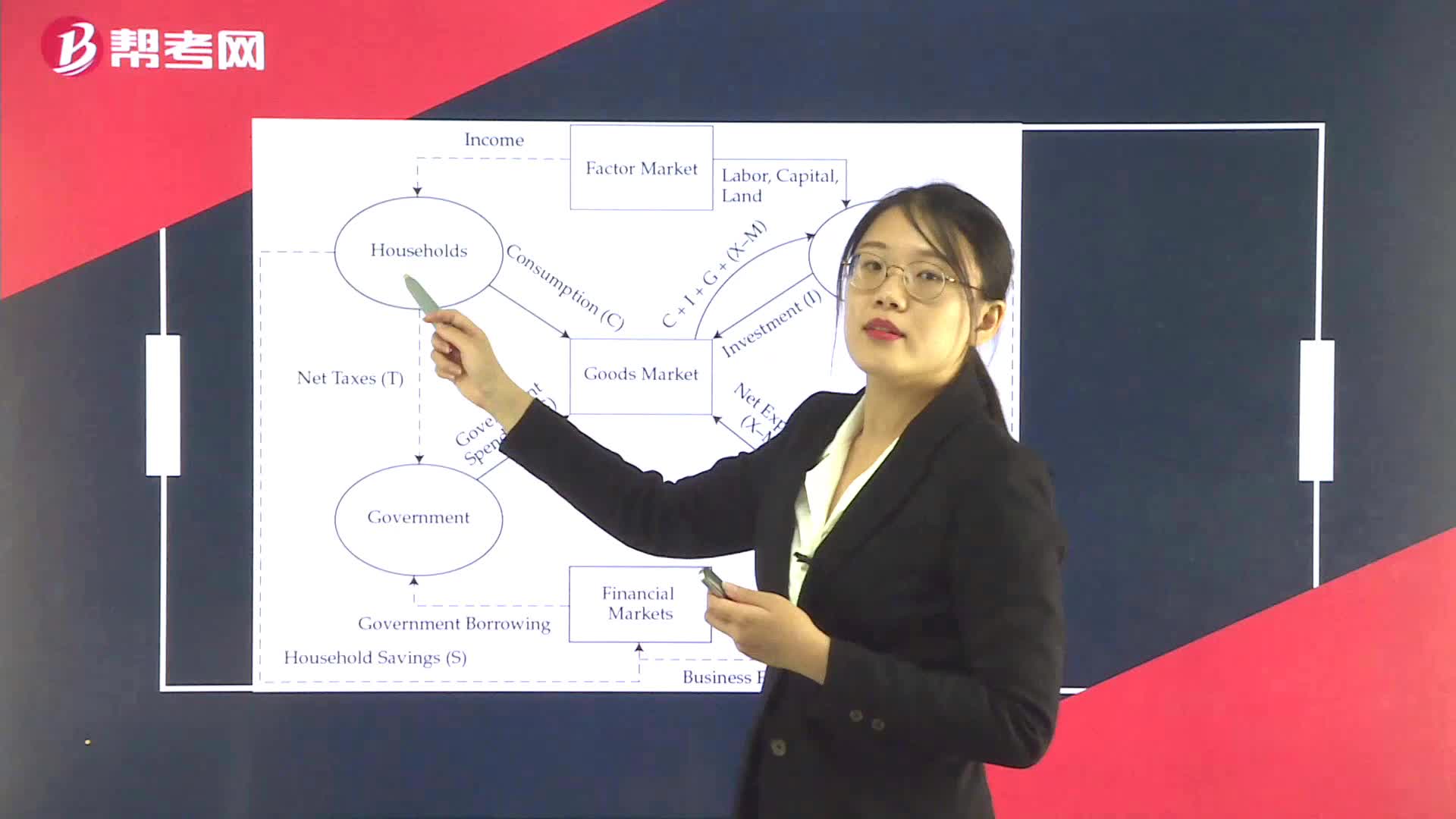
Output, Income, and Expenditure Flows

Imports and Exports

GDP and GNP

Marginal Revenue, Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization
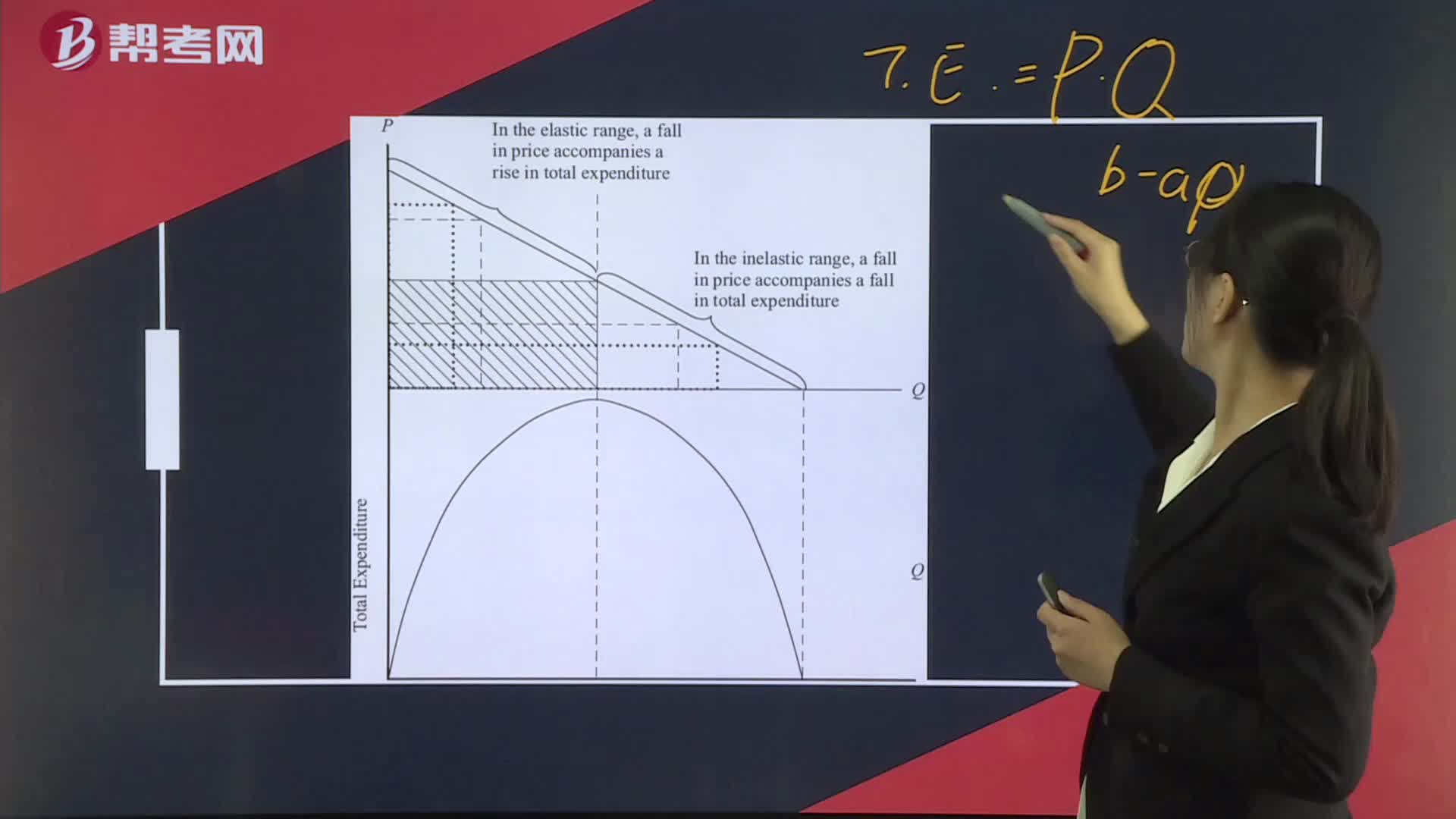
Elasticity and Total Expenditure

Absolute and Comparative Advantage

Economic Profit and Accounting Profit

Long-Run Equilibrium in Perfectly Competitive Markets

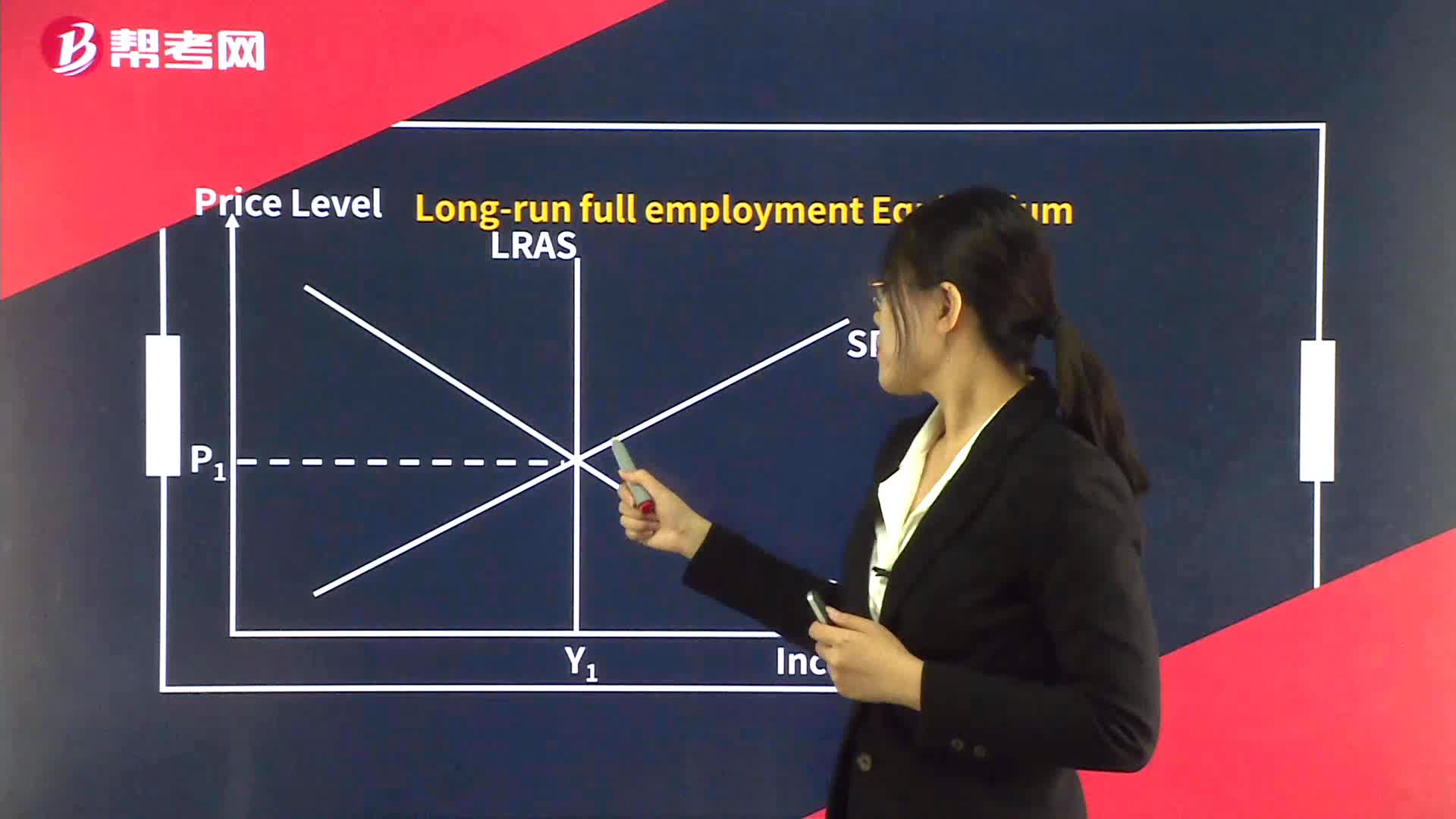
Shifts in the AD and AS curves and Equilibriums

Long-Run Equilibrium in Oligopoly Market

Financial Notes and Supplementary Schedules

下載億題庫APP
聯系電話:400-660-1360