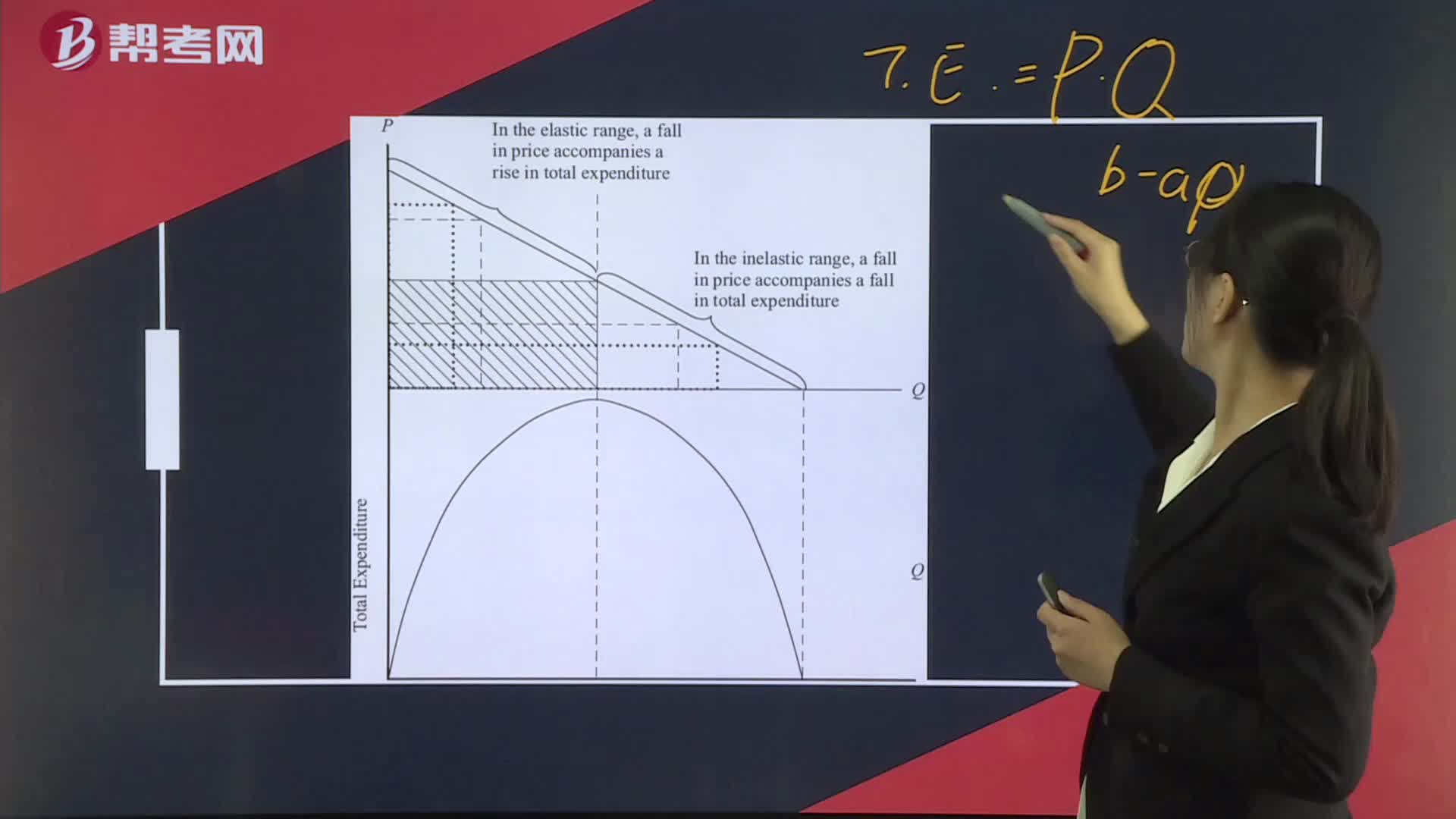
Elasticity and Total Expenditure

Absolute and Comparative Advantage
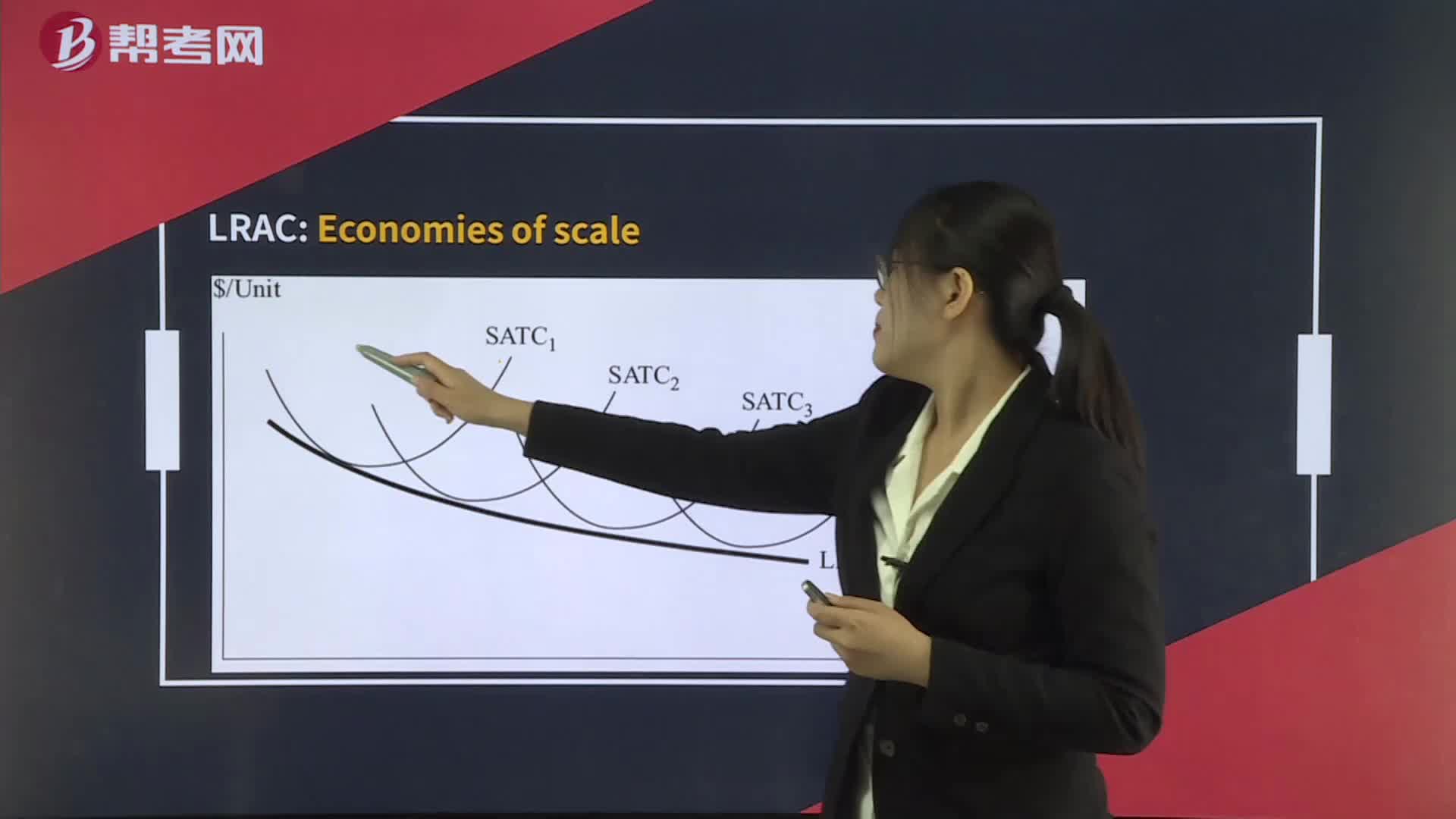
Economies of Scale and Diseconomies of Scale

Economic Profit and Accounting Profit

Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand

Shifts in the AD and AS curves and Equilibriums

Financial Statements and Supplementary Information

Financial Notes and Supplementary Schedules

Equilibrium GDP and Prices

The Relationship Between Fiscal and Monetary Policy
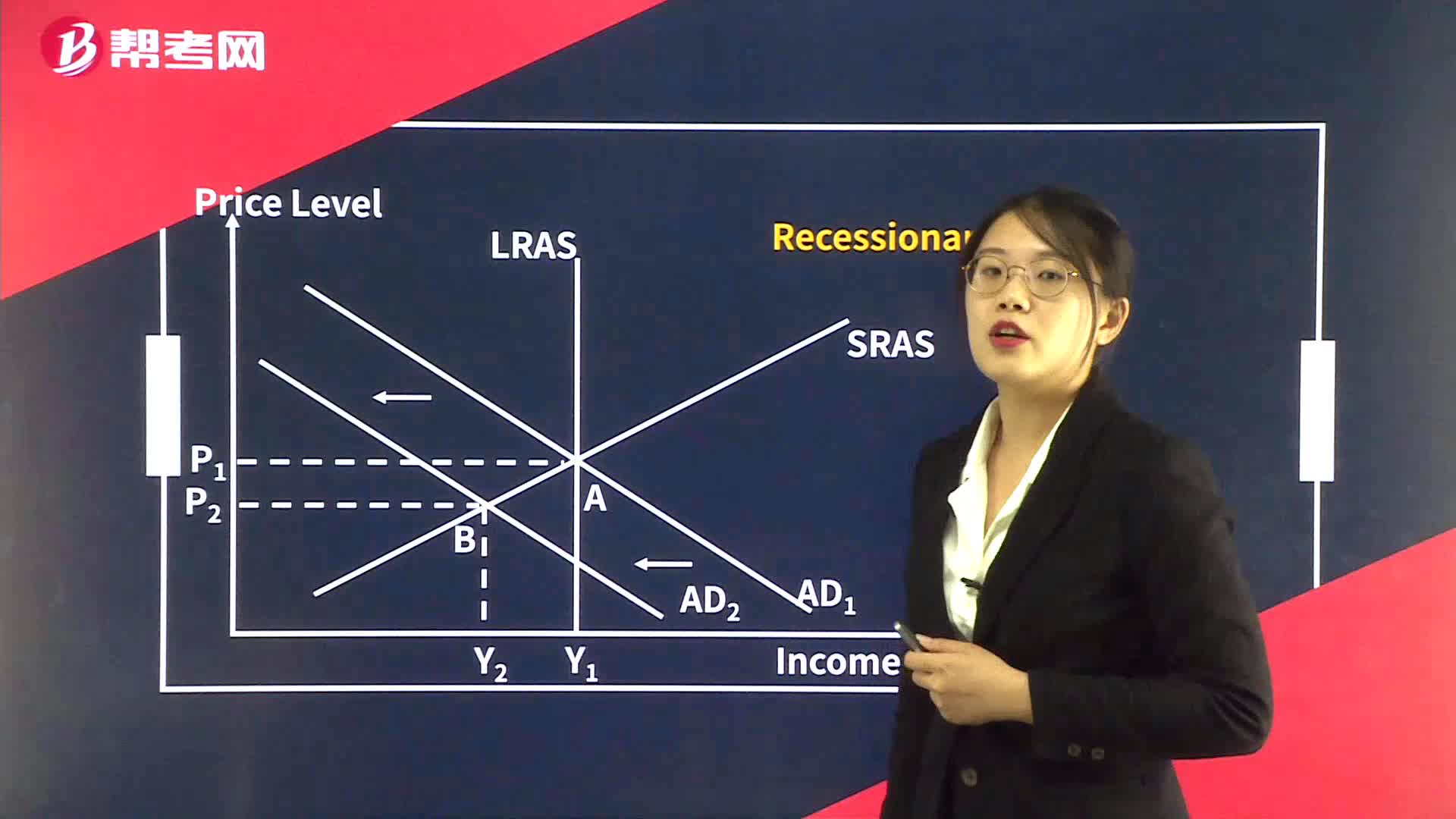
Equilibrium GDP and Prices - Recessionary Gap

Price Indexes and Their Usage

下載億題庫APP
聯系電話:400-660-1360